Welder
Welder & Coded Welder
Welding is a skilled role that can be based either within a workshop environment or based on site. As a Welder there are various types of welding methods available these include:
MIG Welding - Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW)
TIG Welding - Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW)
Stick Welding - Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW)
Flux Core Welding - Cored Arc Welding (FCAW)
Positional Welds ASME IX & 6G
Welding is separated up into different positions. To become a coded welder you will need to be coded in these positions prior to working on a project, this will be based on a pre-approved process for the project usually completed by the project manager within the engineering company.
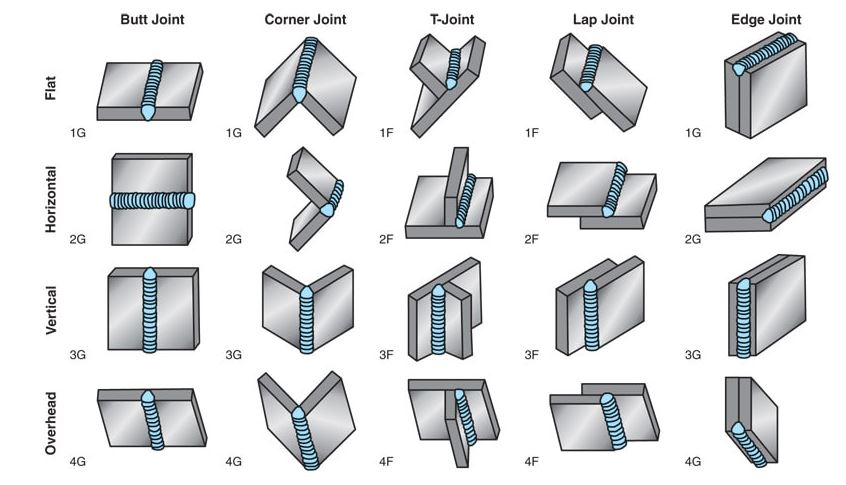
Plate Welding
In plate welding there are 4 positions
– 1G (Flat Welding Position).
– 2G (Horizontal Welding Position).
– 3G (Vertical Welding Position).
– 4G (Welding Position Overhead or Overhead)
Pipe Welding
In pipe welding there are additional positions and complexity to be taken into account they are as follows:
1G Pipe Welding (Horizontal Pipe & Horizontal Welding Position).
2G Pipe Welding (Vertical Pipe & Horizontal Welding Position).
5G Pipe Welding(Horozontal Fixed Pipe & Vertical Welding Position).
6G Pipe Welding(45 degree Fixed Pipe)
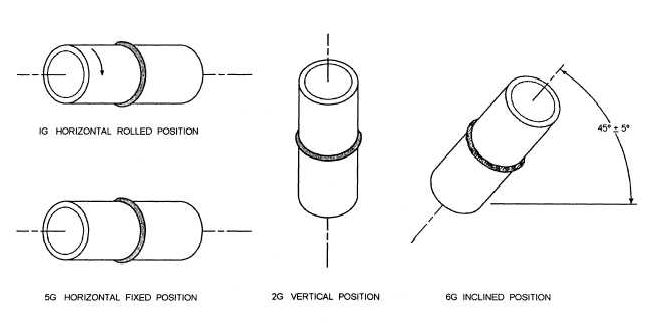
6G welders are in the highest demand and are highly skilled welders, some contractors will complete their own ASME IX or BS EN test, however most contractors will complete a weld test prior to the start of each project. By completing a 6G weld test this will cover you for all of the other positions as well.